Low-code development has evolved from a niche productivity shortcut into one of the most influential forces shaping software outsourcing. As enterprises face mounting pressure to deliver software faster, reduce costs, and maintain agility, low-code frameworks are becoming a central part of outsourcing strategies.
Rather than replacing developers, these platforms multiply their efficiency, allowing outsourced teams to focus on architecture, data models, and integrations while visual tools and automation handle much of the repetitive work. For businesses, this means shorter MVP timelines, smoother scaling, and greater visibility over outsourced projects. The following five trends explain how low-code is redefining the outsourcing model in 2025.
1. Enterprise-Grade Maturity of Low-Code Platforms
Low-code frameworks have matured from departmental productivity tools into strategic enterprise platforms. This transformation is backed by real market momentum: according to Roots Analysis, the global low-code development platform market is projected to reach USD 32.8 billion in 2025 and expand to USD 348.6 billion by 2035, growing at a 26.66% CAGR.
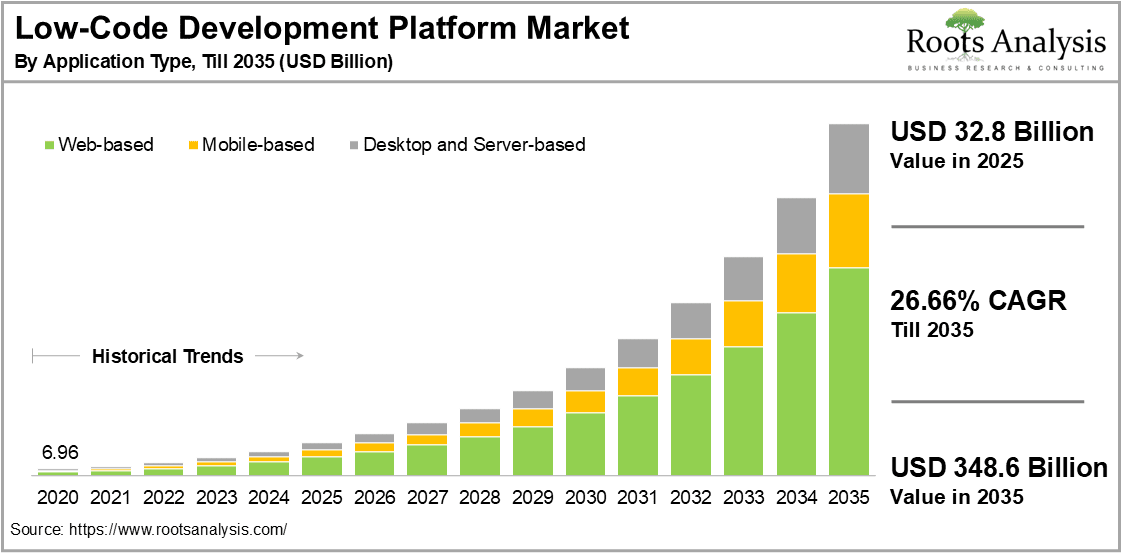
Global low-code market growth by application type, showing 26.66% CAGR till 2035. (Source: Roots Analysis)
This explosive growth reflects how enterprises now view low-code as a core technology for scalable software delivery, not merely a quick-fix tool. The maturity of platforms like OutSystems, Mendix, and Microsoft Power Apps allows outsourcing providers to manage complex workflows, multi-cloud integrations, and regulated data environments through visual configuration instead of manual scripting.
For outsourcing models, this evolution changes the business logic entirely. Instead of billing purely for developer hours, service providers increasingly deliver outcome-based engagements focused on deployment speed, integration stability, and lifecycle performance. This mirrors a broader shift in enterprise SaaS toward value-linked collaboration as discussed in Twendee’s analysis of outcome-based pricing models.
Ultimately, enterprise-grade low-code systems have become the backbone of hybrid outsourcing, where visual development and full-stack customization coexist to balance agility, control, and compliance.
2. AI Integration: The New Driver of Automation and Quality
AI has become the defining layer of efficiency within modern low-code ecosystems. Where low-code once depended on rule-based logic and prebuilt templates, AI now automates code generation, predictive testing, and process optimization, turning what was once a visual builder into an intelligent co-developer.
According to a survey by App Builder, 76% of professionals believe AI will make low-code and no-code tools more efficient, while only 16% think AI could replace them altogether. This indicates a strong consensus that AI acts as an accelerator, not a disruptor, amplifying the capabilities of both developers and outsourcing teams.
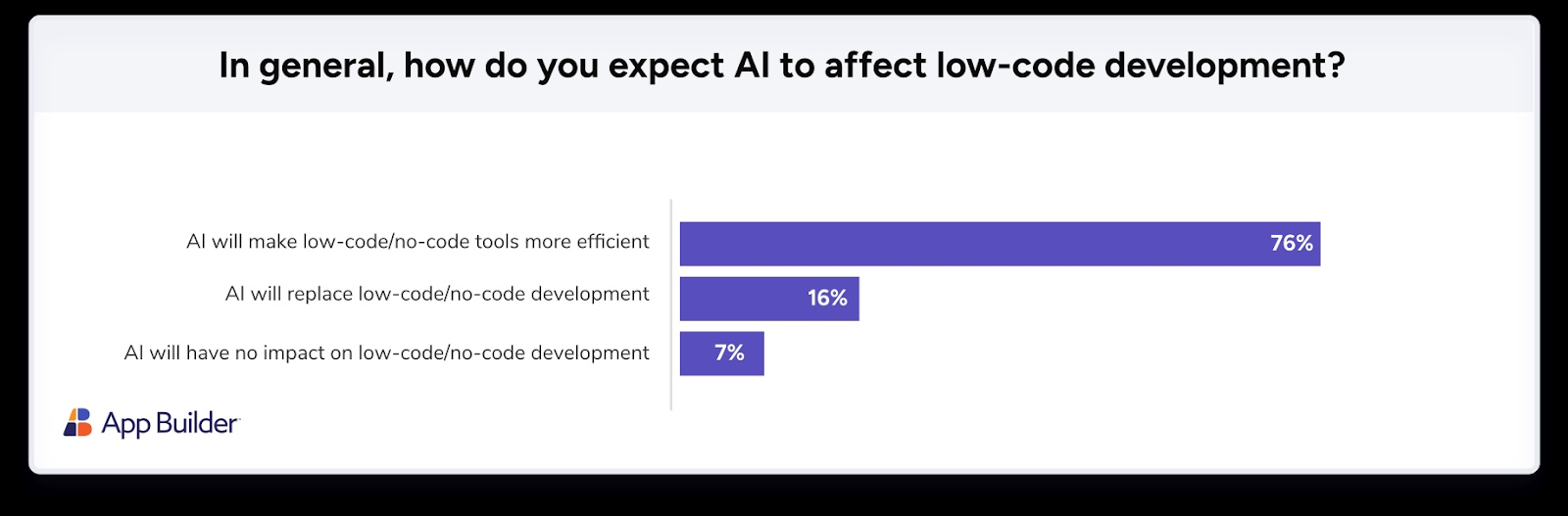
AI integration drives efficiency in low-code development, with 76% of professionals expecting higher productivity. (Source: App Builder)
Leading platforms like Appian, OutSystems, and Mendix have integrated AI copilots that automatically generate logic flows, detect inefficiencies, and suggest code improvements. In practice, this helps outsourcing providers reduce QA cycles, improve delivery predictability, and maintain higher levels of code consistency across global teams.
IDC’s 2025 analysis further notes that AI-assisted low-code environments can cut time-to-market by up to 50% for enterprise software projectprojects, a measurable outcome that directly impacts outsourcing efficiency. Combined with automated model validation and quality monitoring, AI integration transforms low-code from a visual productivity tool into a full-fledged automation engine capable of delivering large-scale digital products with industrial precision.
3. Citizen Development and the Shift in Outsourcing Roles
The rise of citizen development, where non-technical employees use low-code tools to build internal solutions, is fundamentally changing how outsourcing operates. It’s not a trend of replacement, but of redistribution: internal teams handle lightweight automation, while outsourcing partners focus on governance, integration, and scalability.
According to Kissflow’s 2024 “Citizen Development Stats and Trends” report:
30% of custom enterprise apps are now created by personnel with limited or no coding skills,
80% of organizations view citizen development as critical to their automation success,and
75% of large companies plan to use at least four low-code/no-code tools as part of their digital strategy.
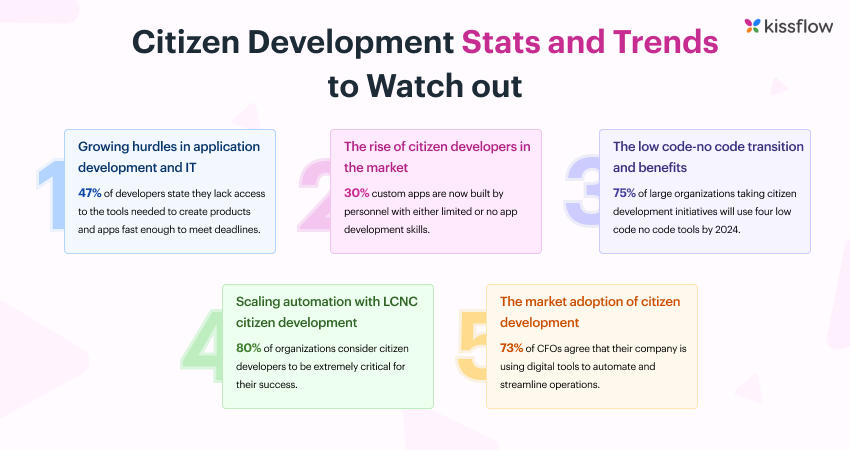
Citizen development statistics showing rapid enterprise adoption and rising importance for automation. (Source: Kissflow)
This shift is fueled by growing backlogs in traditional IT departments - 47% of developers report lacking the tools or bandwidth to meet deadlines and an urgent need to scale automation beyond specialized teams. For outsourcing providers, the opportunity now lies in orchestrating and securing this distributed creativity, ensuring that citizen-built solutions align with enterprise standards for performance, data compliance, and integration.
Leading outsourcing firms are adopting a “center of excellence” approach building reusable low-code templates, establishing approval workflows, and embedding governance APIs that empower business users without losing control. In effect, outsourcing evolves from “building software” to architecting frameworks for innovation, where professional and citizen developers co-create under a shared governance model.
4. Security and Compliance as Built-In Design Principles
Security used to appear at the end of the software lifecycle — a final testing phase that often came too late to prevent vulnerabilities.
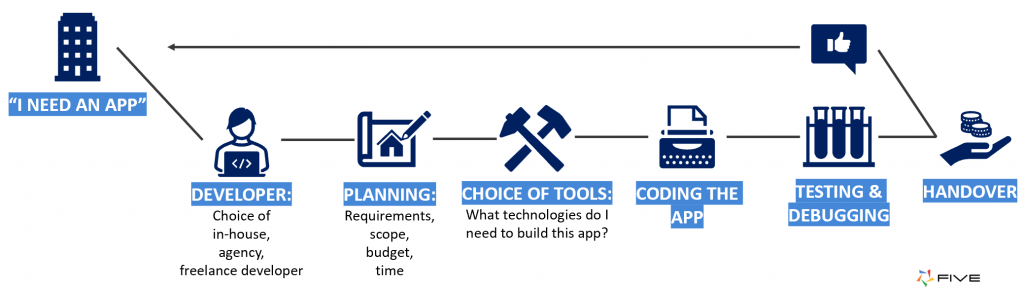
Traditional app development workflow showing security checks occurring only during testing and handover. (Source: FIVE)
In a traditional outsourcing model, this linear structure (plan → code → test → deliver) created two persistent issues: delayed risk discovery and compliance silos. Security teams worked separately from developers, leading to costly rework and fragmented governance especially when multiple vendors or third-party APIs were involved.
Low-code platforms are now closing this gap by embedding security and compliance automation directly within development environments. Instead of patching risks post-launch, teams define policies before a single line of logic is built.
Platforms like OutSystems, Appian, and Power Platform now offer built-in controls for data encryption, access management, and change tracking that continuously enforce governance from design through deployment.
According to a 2024 Statista survey, 63% of enterprises cited security as their top concern when adopting low-code. This pressure has accelerated the adoption of DevSecOps-ready frameworks — where vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and compliance mapping are integrated into every build cycle.
For outsourcing providers, this is more than a tooling update; it’s a process transformation. Security is now part of project architecture, not a post-project audit. By defining policy-as-code, outsourced teams can automate compliance across regions (e.g., GDPR in Europe, HIPAA in the U.S.) and deliver audit-ready systems from day one.
This shift transforms outsourcing into a continuous assurance partnership, where low-code speed and enterprise-level trust can finally coexist. Instead of “test at the end,” the mindset becomes “secure from the start.”
5. Composable Architectures and Modular Delivery Models
The move from monolithic to composable architecture represents one of the most strategic shifts in enterprise software development.
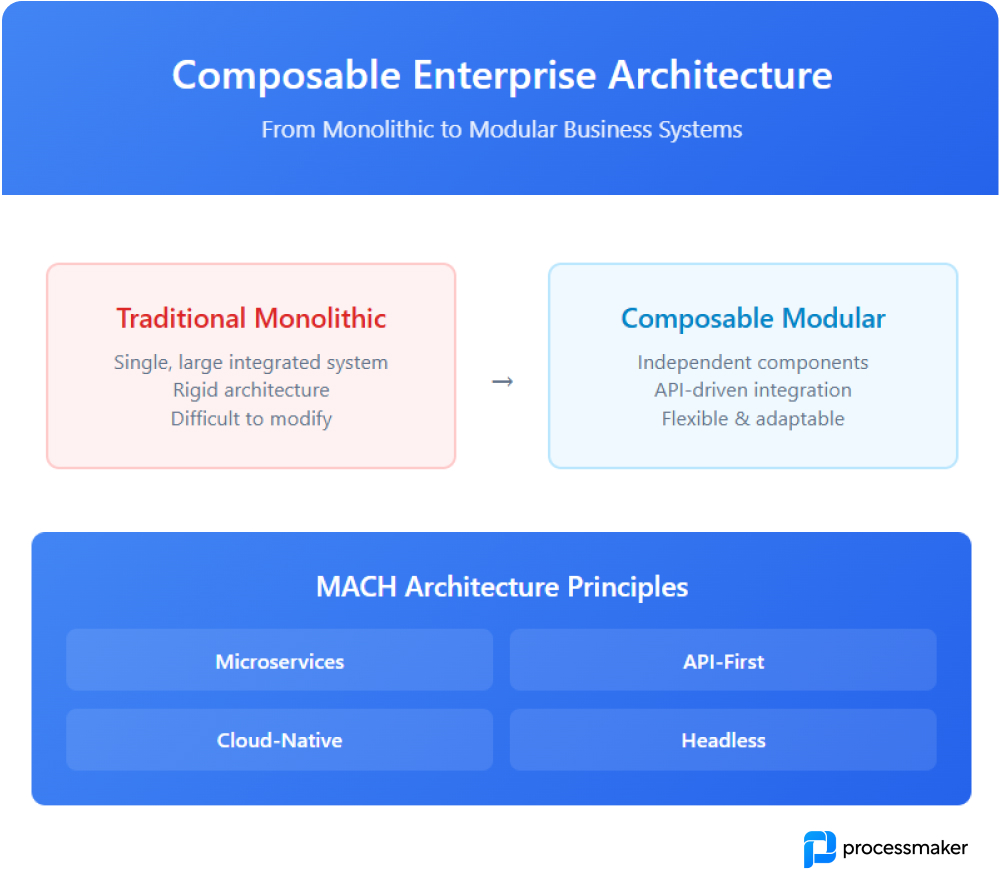
Composable architecture enables modular, API-driven systems that replace rigid monolithic software with flexible, cloud-native components. (Source: ProcessMaker)
In monolithic systems, every module data, logic, interface is tightly coupled, making updates slow and costly. Outsourced teams working under this model often struggle with interdependencies that limit scalability.
Composable architecture solves this by using independent, API-driven components that can be developed, deployed, and scaled separately. Teams can innovate faster and adapt to business changes without refactoring entire systems.
Key foundations of this model include:
MACH principles: Microservices, API-first, Cloud-native, and Headless design ensuring modularity and interoperability.
Agility and time-to-market: Gartner forecasts up to 80% faster feature delivery for enterprises adopting composable design.
Lower technical debt: Modular architecture simplifies maintenance and upgrades over time.
For outsourcing providers, composability transforms engagement models. Instead of one-time delivery, teams now manage continuous modular evolution maintaining and optimizing digital ecosystems across platforms. This enables enterprises to:
Localize or customize features without system downtime.
Integrate third-party tools seamlessly.
Scale incrementally with predictable costs.
Low-code platforms like Mendix and OutSystems further accelerate this shift, allowing outsourcing teams to visually assemble APIs, workflows, and microservices. The result is a hybrid delivery model combining the efficiency of outsourcing with the agility of in-house development.
Conclusion
Low-code development is transforming software outsourcing from labor execution to value creation. By merging AI-driven automation, composable architecture, and built-in security, it enables outsourcing models that are faster, leaner, and enterprise-ready. As organizations demand rapid delivery without compromising control, low-code becomes the foundation for scalable and adaptive software ecosystems.
Discover how Twendee enables this shift, and stay connected via LinkedIn and Facebook.